PayPal
Q4 22’ SUMMARY
While the prevailing sentiment indicates that PayPal is entering a materially lower growth state due to maturation, the vast platform enhancements are an objective counter to this false narrative. The business continues rolling out feature after feature that enhances the platform’s utility thus making PayPal top of mind for consumers across an increasing number of transaction types. PayPal has introduced savings, bill pay, new forms of giving, more ways to send international remittances, new debit and credit cards, as well as rewards and customized deals. The business is essentially integrated disparate services into one app, which is a demonstrated value add for consumers who have shown a desire for all-in-one solutions.
While the e-commerce market forces have affected PayPal’s growth rate, it is essential to step back to appreciate the compounded growth rate as well as the fact that growth is still healthy. PayPal’s growth was driven by strong user acquisition, platform usage, and spending increases. The business continues to demonstrate the ability to capture meaningful portions of global consumer spending. While there were headwinds in the international business, PayPal’s domestic business more than offset the weakness abroad.
PayPal’s leadership deserves credit for their ability to set aggressive margin targets then hitting them well ahead of schedule. This is especially the case due to the fundamental changes necessary to drive the planned efficiencies. The prevailing market sentiment places a high degree of doubt that management has the capabilities to set achievable targets and hit them.
Overall, PayPal has a unique position in a massive market with an expanding TAM. The business continues to develop and launch innovations that attract new users while stimulating increased spending from existing users. PayPal is a great example of leveraging market positioning to integrate innovations that drive durable compounding growth.
Source: PayPal
“2022 was a transformative year for PayPal. We invested in our platform to better serve our customers, while focusing and
streamlining our business. We will continue this work throughout 2023, and I am confident that we are well positioned
to utilize our unique assets to remain a market leader in digital payments”
Key Takeaways from Q4 22’
Key Takeaway 1- Paypal’s platform continues driving engagement
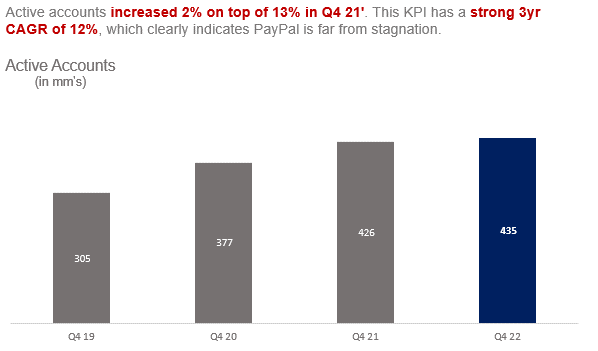
Engagement on the platform outpaced account growth as PayPal is acquiring greater numbers of users who are engaging more and more on the platform.
The success of unbranded payment processing via BrainTree has given management the evidence needed to fully ramp out PayPal’s general unbranded offering.
Key Takeaway 2- the business drove growth across portoflio
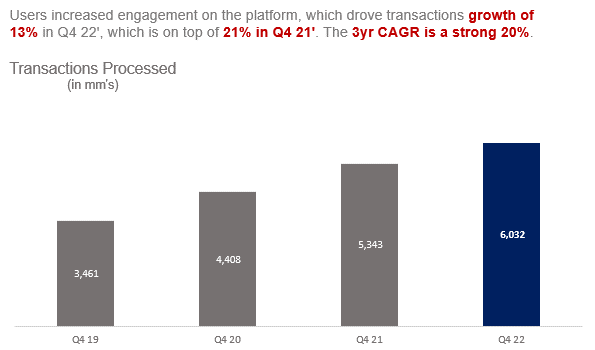
PayPal’s core transaction revenues increased meaningfully in Q4 22’ as the business monetizes digital commerce.
PayPal’s secondary Other Value Added Services revenues continued to grow at a fast pace, which is being driven by the business’ capitalization on the Buy-Now-Pay-Later trend.
Key Takeaway 3- consumer spending is strong even post-pandemic
E-commerce spending continued to demonstrate strong momentum in Q4 22’ even after the massive adoption during the pandemic.
Globally, e-commerce is expected to continue taking share from brick and mortar retail, which is expected to continue growing as well.
GROWTH TRENDS
growth Factor 1- balanced global momentum
While PayPal has a large global business, the domestic business is core to the company especially in the last couple of years. In Q4 22’, the domestic business drove the company’s growth as the international business continued to face headwinds that emerged in 2H 21’. This divergent performance was not enough to derail the business’ growth as the domestic business is materially larger and generated growth that more than compensated for the temporary international headwinds.
The international business is still a material contributing force to PayPal’s growth in recent periods. In Q4 22’, the international business generated accelerated growth from Q4 21’ levels as this business started to recover from sharp headwinds in recent periods. Trends abroad were positively impacted by a return to spending growth after headwinds related to longtail pandemic impacts as well as volatility related to geopolitical tensions. Both of these forces had a reduced impact in Q4; however, the business still has ways to go before it is back on track. This is a tailwind for the business in 23’ as there is no evidence that the international business will not continue returning to strong growth that is inline with the domestic business. In fact, it could easily be stronger given PayPal’s position in cross border transactions and the larger international TAM.
growth Factor 2- robust platform monetization
PayPal’s platform monetization drove momentum in the core transactions business. PayPal’s business model places the business in a central role in the digital commerce megatrend. The platform enables buyers and sellers to digitally transact with each other in a seamless manner. PayPal has massive scale, which is a product of the company’s first mover advantage. The business is designed to monetize digital commerce by way of charging transaction fees to buyers and sellers that commercially engage with each other using PayPal’s proven technology.
PayPal is driving strong performance across many operational and financial metrics by rolling out innovation that reduces friction for the end user at checkout. This is a key utility consumers look for when choosing how they choose to pay for products or services. Some features being introduced are passwordless checkout, one click native in-app checkout, and next generation of advanced checkout using PayPal’s data and AI capabilities. The business is already migrating legacy integrations to the new architectures, which will take time given the immense scale of the business. This means that the benefits of platform enhancements will have a long tail thus supporting compounding growth over the next several years.
PayPal is already realizing new sales and incremental volume from existing accounts that can be attributed to the changes in architecture and platform capabilities. This is clear evidence that the business understands what drives user engagement and knows how to deliver the utility demanded. The success of unbranded payment processing via BrainTree has given management the evidence needed to fully ramp out PayPal’s general unbranded offering. This will be targeted to the SMB segment of the merchant base. Additionally, the business’ recently launched PayPal Complete Payments (PPCP) will be materially expanded to position the business to serve a market that has a $750bln TAM, which the business had not been able to access.
Trends are strong in Q1 23’ across the business with momentum in branded payments, Braintree payments, unbranded, and BNLP. Braintree is poised to continue driving growth above the company average as the product is adopted for more merchant volumes. This is driven by the utility that merchants realize with Braintree, which includes superior auth rates that are almost 4ppts better than competing solutions. PayPal will be rolling out the PPCP to SMB in a meaningful way in 23’ after seeing traction with unbranded in 22’. This is to provide merchants with the capability to essentially white label PayPal’s technology.
The PayPal Commerce Platform positions the business to offer a full payment stack to merchants, which offers features that is designed to drive utility above competing solutions. Typically, merchants will use several vendors to provide end-to-end support to process a transaction. The business’ ability to predict services that users will want and then deliver those services is a major reason to be bullish on the business. In fact, PayPal has shared that user who adopt new services end up spending about 25% more than they did before the service.
PayPal’s growth was largely driven by the newer lines of business, which include Braintree and Venmo. Additionally, the business generated strong growth in the other value added services as PayPal demonstrates an ability to upsell the massive user base. The growth in other value added services led to the business driving take rate higher as customers pay more for these services. While the Value Added Services business is not nearly as important to the business as transaction services, it is still a meaningful contributor to PayPal’s growth and profitability. The company has integrated services outside of core payments into the business model, which is a wise move given PayPal’s proximity to consumers and businesses. The business continued to rebound from the massive blow dealt by COVID in Q2 20’.
BNPL has been a highly valuable offering for the business as it has been credited for driving a substantial lift in spending. The fact that the stock is cheaper than it was pre-BNPL is an astounding reality as this offering has considerably expanded PayPal’s opportunity. This can only be the case if the bears think that the business will not realize this opportunity, which is simply a baseless point of view based on information and data reflecting the reality of PayPal’s BNPL strength.
growth Factor 3- Platform engagement growth
PayPal’s payment platform generated strong results driven by increased scale and spending. PayPal continues to defy limits by compounding at scale despite the business’ decades long tenure. The platform demonstrated strength across virtually every metric outside of average transaction size; however, this was more than offset by growth in users and growth in average number of transactions. This drove material spending growth per active account in the quarter, which translates to revenue for the business. Overall, PayPal’s strength is driven by the platform’s over 8x greater presence compared to peers. This makes consumers 2x as likely to purchase on a given site due to the trust consumers have for the widely known brand.
Customers are using PayPal much more than they have in the past driven by the combined effect of discretionary momentum, e-commerce strength, PayPal’s deep digital footprint, and friction-reducing enhancements over the last couple of years. This has led to transactions per active accounts growing at strong CAGR, which indicates that users are opting to use PayPal for payment processing in more instances. Once again, the bear thesis significantly discounts the engagement strength that these trends clearly indicate. PayPal is far from maturity, especially as the share of spending that occurs online continues to represent more and more of total spending.
PayPal is driving strong performance across many operational and financial metrics by rolling out innovation that reduces friction for the end user at checkout. This is a key utility consumers look for when choosing how they choose to pay for products or services. Some features being introduced are passwordless checkout, one click native in-app checkout, and next generation of advanced checkout using PayPal’s data and AI capabilities. The business is already migrating legacy integrations to the new architectures, which will take time given the immense scale of the business. This means that the benefits of platform enhancements will have a long tail thus supporting compounding growth over the next several years.
PayPal is aggressively upgrading the merchant base to the business’ most advanced checkout technology. This can be seen by the rate at which top 100 merchants are being migrated to the new architecture. In 21’, 20% of the top 100 were using it, 30% of the top 100 were using it, and the business expects about 50% of the top 100 to be onboarded. This is a highly valuable development as the modernization of the checkout experience drives transactions for merchants while making purchasing easier for consumers. As a result, PayPal stands to gain even more share of the payment processing wallet share. The bears are not appreciating the utility of PayPal’s innovations, which means they are unaware of the financial benefits that will follow from these new technologies.
PayPal has a gem in the form of the business’ massive accounts and active accounts. While PayPal has over 190mm monthly active accounts, this number is about half of the accounts portfolio. The disparity is due to many people signing up for PayPal at some point in their commercial lives only to allow usage to lapse. This is extremely valuable as it means that the business has a vast number of potential active user growth from getting lapsed users to reengage. Additionally, the massive active user base represents a major base of economic potential that can be harvested in the form of higher engagement. While PayPal has split focus between getting new users and driving engagement with existing users, the business is now focusing engagement in the form of lapsed users turning into monthly active users as well as getting active users to use PayPal more. This is the reason for PayPal not being as focused on acquiring new users as the business can generate growth for many years just by harvesting the base it already has amassed.
Additionally, the bear thesis does not appreciate the material utility that users find in PayPal’s new SDK and API functionality which makes the payment process much more seamless. Merchants and consumers have shown a strong preference for being able to finalize transaction without leaving the site as well as being able to provide a consistent experience. This can be seen in the ~10% conversion lift when mobile SDK’s are integrated. PayPal’s ascension to the top 10 requested SDK and API on developer sites is a strong piece of evidence that the decision to allow such integrations provide a great deal of utility, which translates into more market share winning opportunities.
OPERATIONAL EFFICIENCIES
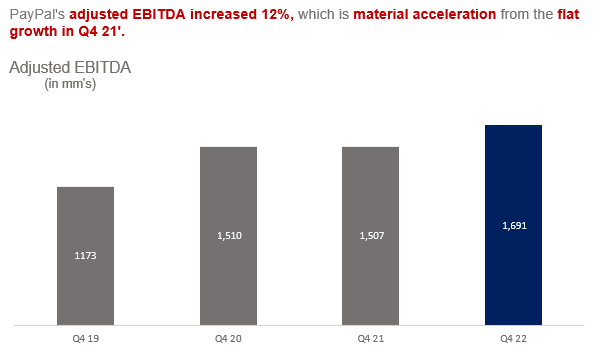
The business drove immense efficiency in Q4 as the significant cost reductions are starting to materialize in operating margins. This is a major blind spot in the bear thesis, which implies that earnings growth is unlikely to outpace revenues for the foreseeable future. In Q4, PayPal’s efficiency drove revenue growth several points above non-transaction related OpEx, which is a major portion of the business’ cost structure. The business has cut costs by over $900mm in 22’ driven by refining organizational focus to be much more targeted in expense allocation. This is a shift from operating without a true focus on efficiency as the business was undertaking simply too many initiatives and projects. Combined with the $4.2bln in share repurchases in 22’, the business is structurally more profitable, which is significant evidence against a bear thesis on PayPal’s trajectory.
While the $900mm in cost savings has driven material margin expansion, the business has identified an additional $1.3bln in savings that can be realized in 23’. This is another piece of evidence that PayPal has a real plan to drive profit growth in the immediate future. In fact, management has communicated that the business is actually ahead of schedule on the $1.3bln in savings for 23’. Furthermore, management has not stopped identifying efficiencies despite the material changes already underway. As a result, management has identified an additional $600mm in cost savings on top of the $1.3bln in 23’.
INDUSTRY TRENDS
PayPal’s business model and scale uniquely positions the business to capitalize on the growing e-commerce megatrend. PayPal is deeply entrenched in the digital payments industry based on the platform’s connection with hundreds of millions of economic participants. In other word, e-commerce’s gain is PayPal’s gain.
Specifically, e-commerce spending in the U.S. increased 7% in Q4 22’, which is on top of 10% growth in Q4 21’. In Q4 22’, e-commerce spend represented 15% of retail spending in the US, which is on par with the 15% representation in Q4 21’. This is especially positive as 20’ and 21’ were strong years for e-commerce spending given the COVID impact on brick and mortar spending.
In 22’, market research firm eMarketer expects e-commerce spending in the US to increase 9% in 22’ after a strong period of growth in 20’ and 21’. Looking out into the medium term, the firm is projecting e-commerce spending to grow at a 5yr CAGR of 11% for the five year period ending 26’, which has reduced by 1ppt since the last update driven by conservatism and strength in brick and mortar trends. This compounded growth is expected to outpace that of brick and mortar spending, which is expected to drive e-commerce as a percentage of total from 15% in 21’ to 20% in 26’.
In 22’, eMarketer expects global e-commerce spending to increase 10% after a strong period of growth in 20’ and 21’. Looking out into the medium term, the firm is projecting e-commerce spending to grow at a 5yr CAGR of 9% for the five year period ending 26’. This compounded growth is expected to outpace that of brick and mortar spending, which is expected to drive e-commerce as a percentage of total from 19% in 21’ to 24% in 26’.
The Buy-Now-Pay-Later trend is expected to continue growing from a user base and payment value perspective. This financing option has truly taken hold in the economy, which bodes well for business’ that contribute to the infrastructure of this novel and classic form of financing. In 22’, eMarket expects BNPL users to grow 56% to reach 79mm in the US. This is a massive increase from the 102% growth in 21’ as more and more consumers adopt BNPL, which is being facilitated by merchants offering the financing type. These users are expected to spend $76bln using BNPL, which is a staggering 77% increase from the $43bln BNPL spend in 21’.
Looking ahead to the medium term, eMarket is projecting users and payment value to grow at a 5yr CAGR of 16% and 27%, respectively. This implies that BNPL users will represent about 40% of internet users in the US, which is a material expansion from the 20% in 21’. Financially, this implies that BNPL will represent about 11% of all e-commerce spend by 26’, which is more than 2x the 5% representation in 21’.
FORECAST AND VALUATION
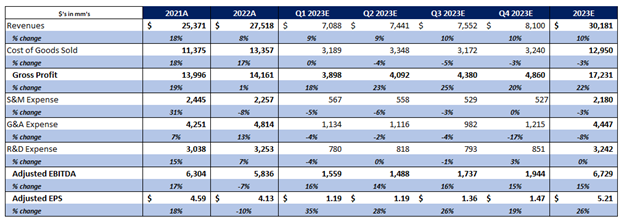
PayPal’s earnings are poised to benefit from the compounding factors of accretion from lower share count and efficiencies driving operating leverage. Management demonstrated a pretty astounding level of confidence in their ability to drive 18% earnings growth in 23’ even in a global recessionary scenario combined with continued inflation pressure. This means that the likelihood of PayPal delivering earnings growth above this “bear case” is much higher than the likelihood of PayPal missing the 18% level. In this scenario, management anticipates revenue growth in the low single digits, which is highly conservative given the numerous drivers ranging from e-commerce recovering from 22’ base effects to benefits from PayPal’s technology rollouts. Trends are already demonstrating strength in Q1 23’ across the business with momentum in branded payments, Braintree payments, unbranded, and BNLP. PayPal is virtually a derivative on e-commerce activity.
PayPal is virtually a derivative on e-commerce activity. The recent surge in e-commerce spending in 20’ and 21’ led to substantial base effects in 22’ as purchasing behavior reflected the shift to more physical commerce. As a result, growth rates of payment processors have moderated given that the basis of revenues (e-commerce) have moderated. This is a circumstantial dynamic that is more reflective of normalization of consumer behaviors rather than an indication that PayPal has reached a growth wall. Importantly, the consumer is still very strong and flexing this strength into 23’, which supports PayPal’s business this year. Going forward, the business is poised to experience accelerated growth as the high base is lapped and more reasonable growth levels become the base that revenues are compared.
PayPal’s efficiency has led to a significant milestone in Q4 22’ in which margins expanded for the first time since Q1 21’, which had the benefit of massive pandemic related tailwinds. Anyone betting against PayPal at this point is very likely to be unaware of this inflection point or the implications for future earnings growth that exceeds revenue growth. PayPal has considerable efficiencies to unlock in the cost structure as the majority of expenses are not volume-based, which means they are either fixed in nature or not directly related to processing transactions. This means there is more leverage from simply growing the topline along with efficiency gains from doing more with fewer resources.
PayPal’s new cost structure emphasizes cutting fat while building muscle. In this analogy, the fat represents activities with unclear and longer duration ROI’s. The muscle represents activities that turn the business’ flywheel is a clear manner. The fact that this means material efficiencies being created indicates that the business had allowed fat to accumulate to the point that it represented a material portion of the cost structure. Importantly, looking at PayPal through the inefficient lens leads to one completely missing the earnings power that the business is already displaying. This reality will only become more obvious in 23’ and beyond. In 23’, margins will also benefit from tailwinds created by geographic expansion of newer technologies and offerings, expansion to SMB of newer technologies, and new value added services (risk-as-a-service, FX-as-a-service, etc.).